Lec 9: Advanced Topics¶
Today we will talk about some miscellaneous but important topics.
Outline¶
- Memory Layout
- Buffer Overflow
- Vulnerability
- Protection
- Unions
Memory Layout¶

- Stack
- Store local variables
- Runtime Stack (8MB limit for Linux)
- Text/Shared Libraries
- Store executable machine instructions
- Note: library codes are stored on the disk (e.g.
malloc,printf). They will be introduced to the program when it first starts executing, via dynamic linking.
- Note: library codes are stored on the disk (e.g.
- Read-only
- Data
- Store static data
- e.g. global variables,
staticvars, string constants - Heap
- Dynamically allocated as needed
- e.g.
malloc(),calloc(),new, etc
Buffer Overflow¶
Example: gets¶
gets gets string from stdin, store it at dest and finally return dest.
/* Get string from stdin */
char *gets(char *dest) {
int c = getchar();
char *p = dest;
while (c != EOF && c != '\n') {
*p++ = c;
c = getchar();
}
*p = '\0';
return dest;
}
Because gets will not check the boundary, and there's no way to specify limit on number of characters to read, gets is prone to have buffer overflow.
Other vulnerable functions¶
strcpy, strcat: Copy strings of arbitrary length.scanf, fscanf, sscanf: when given%sconversion specification.- the same as
gets
Code Injection Attack¶
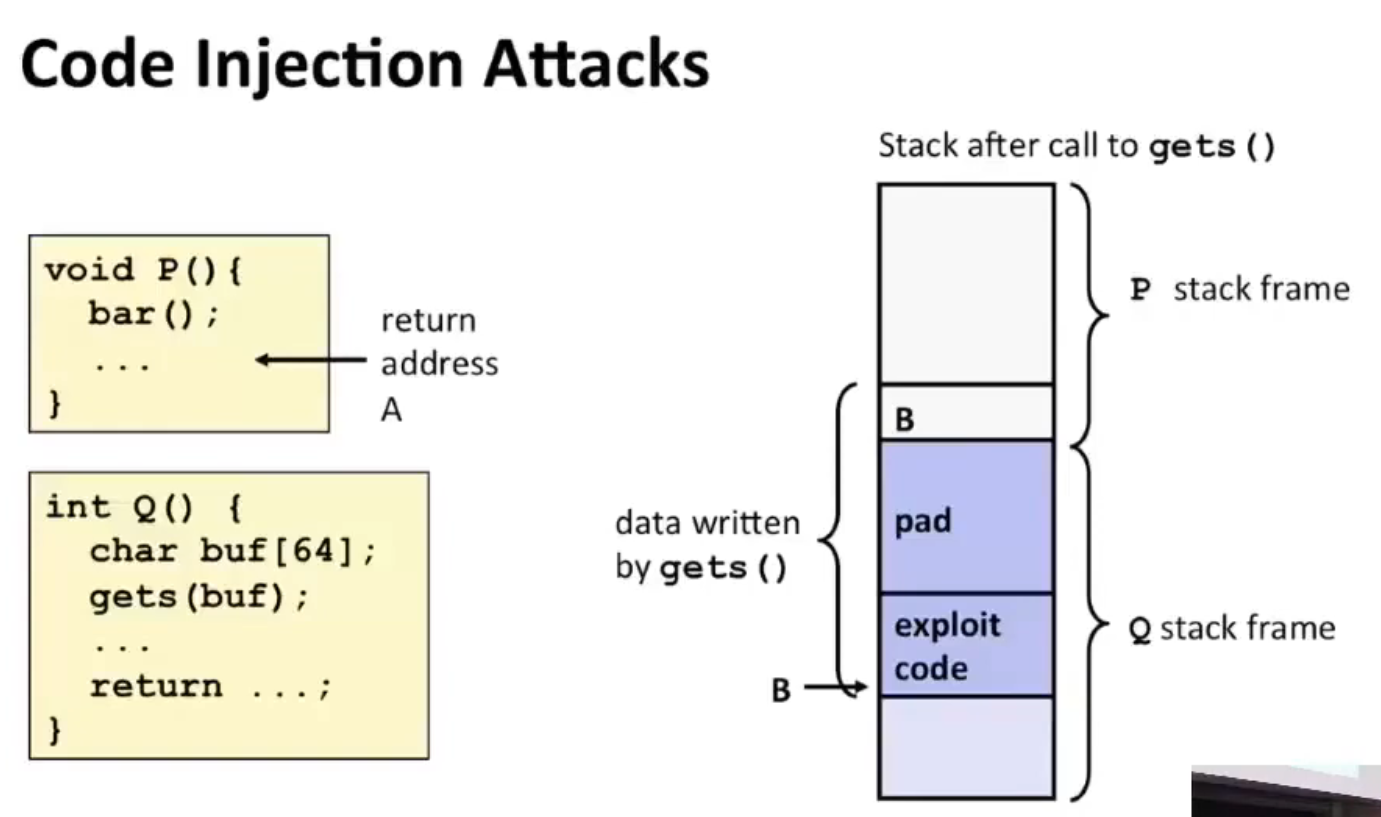
typo:
bar()should beQ()
- Input string contains byte representation of
- executable code
- padding
- ret address
- When
Q()gets returned, it will go to addressBand start executing the exploited code. - Note the return address is stored in the caller's frame.
Sidenote: Worm vs. Virus¶
| 特性 | 蠕虫 | 病毒 |
|---|---|---|
| 定义 | 蠕虫是一种自我复制的恶意软件,它可以在网络中自我传播,无需附着在宿主文件或者其他程序上。 | 病毒是一种恶意软件,它需要附着在宿主文件或者其他程序上才能传播。 |
| 传播方式 | 蠕虫可以自我复制并通过网络自我传播,无需用户交互。 | 病毒需要用户交互(如打开文件、运行程序)才能传播。 |
| 影响 | 蠕虫主要通过消耗系统资源(如网络带宽、内存)来影响系统性能。 | 病毒可以对系统文件进行修改、删除,甚至窃取用户数据。 |
| 自我复制 | 蠕虫可以自我复制,并在没有用户知情的情况下在网络中传播。 | 病毒需要附着在宿主文件上才能复制自身。 |
Return-Oriented Programming¶
Since stack can be randomized and inexecutable, we need to use the present code gadgets instead of our own codes.
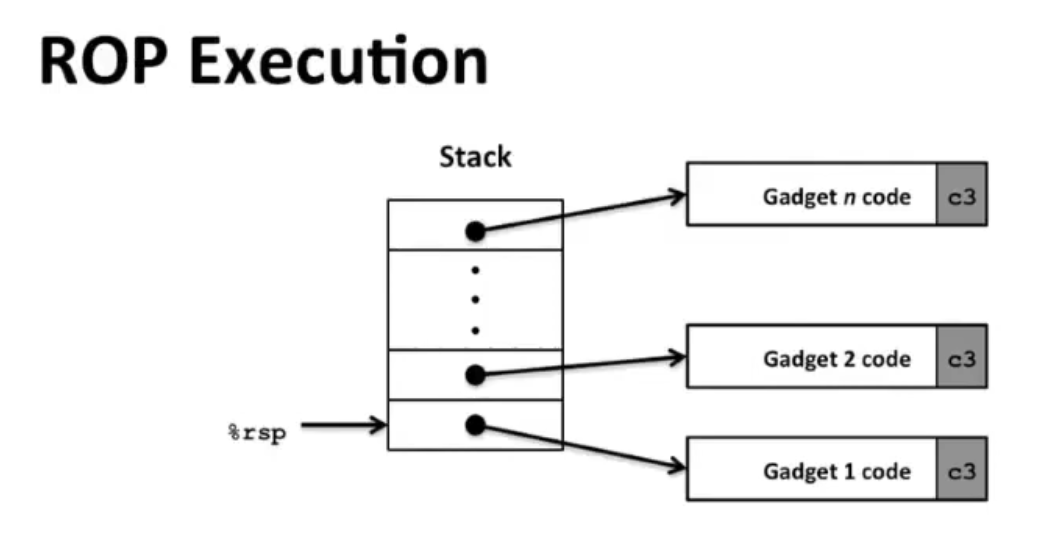
- Trigger with ret instruction
- Will start executing Gadget 1
- Final
retin each gadget will start next one
Protection¶
Avoid Overflow Vulnerabilities in Code (!)¶
- Use
fgetsinstead ofgets - Use
strncpyinstead ofstrcpy - Don't use
scanfwith%s - use
fgets! - or at least use
%nswherenis a suitable integer - ...
System-Level Protection¶
- Address space layout randomization (ASLR) is an oft used technique to protect system from this sort of attack.
Main Idea: apply a random address offset to the stack each time you run the program, so you can't predict where to return.
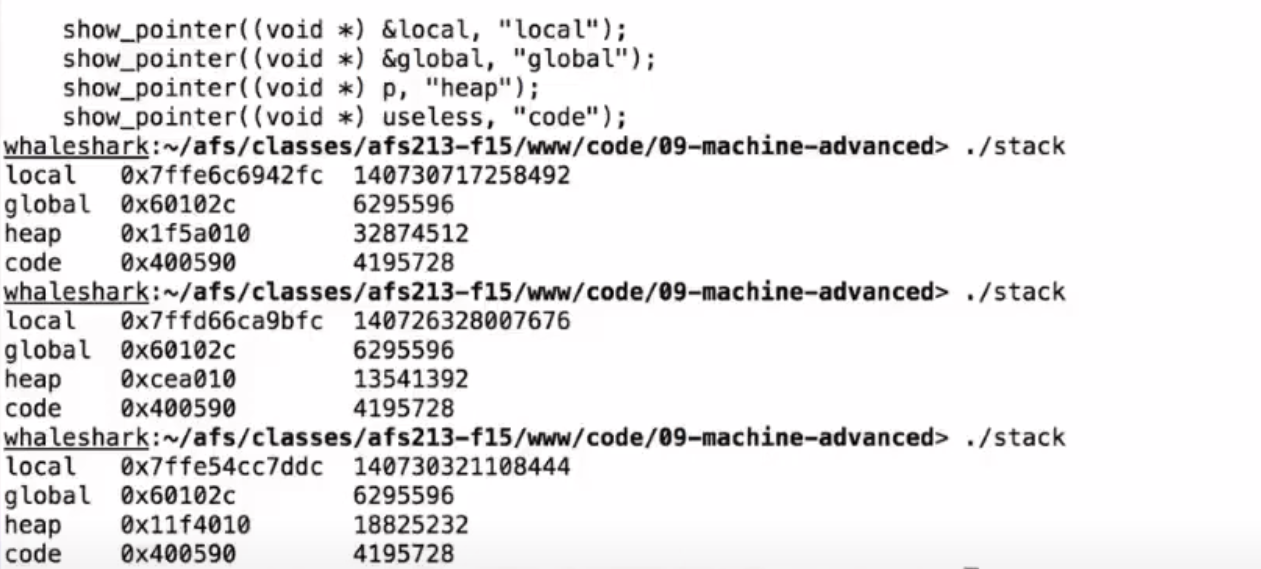
As shown in the image, global is in data and useless is in text, so they won't vary.
But local is in stack and p is in heap, so they vary.
-
pvaries as well, sincemallocalso has its own random implementation. -
Nonexecutable code segments
Main Idea:
- In traditional x86, you can mark a region of memory as either "read-only" or "writable".
- You can execute anything that is readable.
- x86-64 added explicit "execute" permission.
-
The stack is marked as non-executable.
-
Stack Canaries
High
Address | |
+-----------------+
| args |
+-----------------+
| return address |
+-----------------+
rbp => | old ebp |
+-----------------+
rbp-8 => | canary value |
+-----------------+
| local variables |
Low | |
Address
echo:
...
mov -0x8(%rbp),%rax # $rbp stores the original %rsp value
xor %fs:0x28,%rax
je 0x5555555551d1 <echo+72>
callq 0x555555555080 <__stack_chk_fail@plt>
leaveq
retq
In order to cause a buffer overflow and manipulate the return address, it is necessary to overflow the canary value, which is generated using a pseudo-random process. By overflowing the canary value, the validity check for the canary fails.
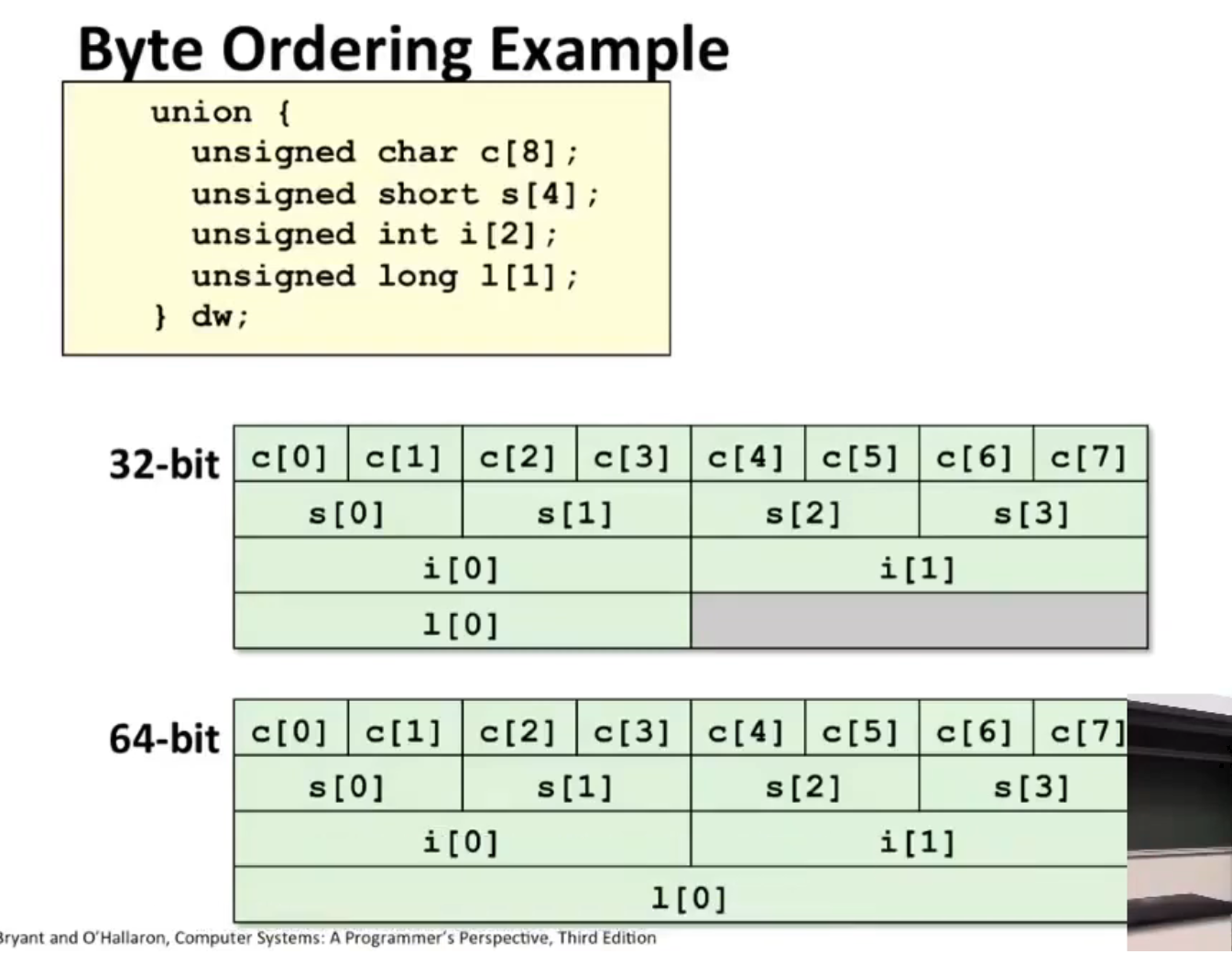
Union¶