Lec 8: Machine Level Programming: Data¶
Array¶
Multidimensional (Nested) Array¶
\[
\begin{bmatrix}
A[0][0] & \cdots & A[0][C-1] \\
\vdots & & \vdots \\
A[R-1][0] & \cdots & A[R-1][C-1] \\
\end{bmatrix}
\]
- Declaration
T A[R][C]
- 2D array of data type T
- \(R\) rows, \(C\) columns
-
Type T elements requires \(K\) bytes
-
Array Size
-
R * C *K
-
Arrangement
-
Row-Major Ordering
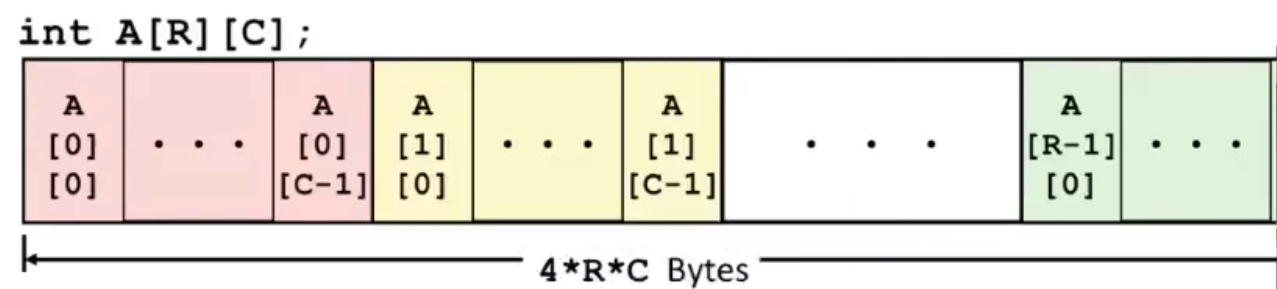
-
Array Elements
- \(A[i][j]\) is at address \(A + (C * i * K) + j * K = A + (C * i + j) * K\)
int get_pgh_digit
(size_t index, size_t digit)
{
return pgh[index][digit]; // = *(pgh + index * C * 4 + digit * 4) = *(pgh + (index * C + digit) * 4)
}
leaq (,%rdi,10) %rdi # (index * 10)
addq %rdi %rsi # (index * 10) + digit
movl pgh(,%rsi,4), %eax # ret_val = *(pgh + ((index * 10) + digit) * 4)
ret
Multi-Level Array¶
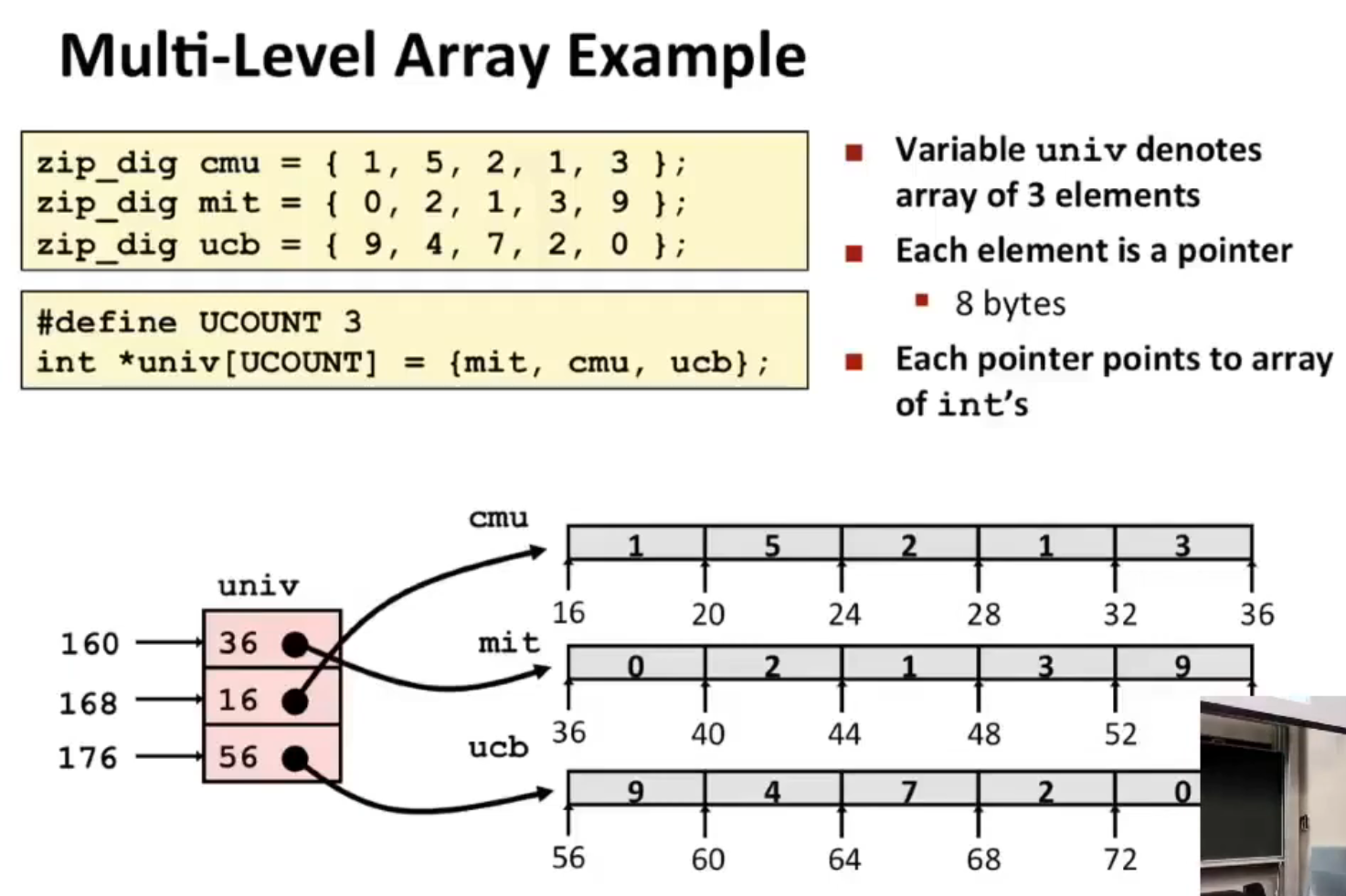
For Multi-Level Array:
int get_univ_digit
(size_t index, size_t digit)
{
return univ[index][digit]; // = *(*(univ + index * 8) + digit * 4)
}
salq $2, %rsi # digit * 4
addq univ(,%rdi,8) %rsi # *(univ + index * 8) + digit * 4
movl (%rsi), %eax # ret_val = *(*(univ + index * 8) + digit * 4)
ret
Note: The code for these two representations are the same, but the assembly codes are different.
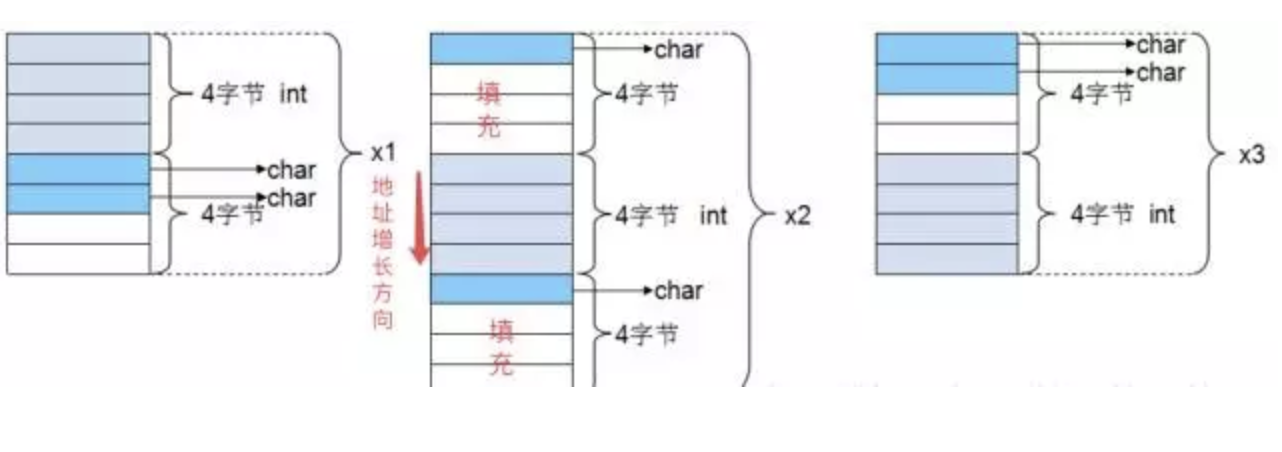
Structures & Alignment¶
规则:
- 结构体第一个成员的偏移量(offset)为0,以后每个成员相对于结构体首地址的 offset 都是该成员大小与有效对齐值中较小那个的整数倍,如有需要编译器会在成员之间加上填充字节。
- 在Linux环境下,linux下默认#pragma pack(4),且结构体中最长的数据类型为4个字节,所以有效对齐单位为4字节
- 结构体的总大小为 有效对齐值 的整数倍,如有需要编译器会在最末一个成员之后加上填充字节。
e.g.
c struct { int x; char y; char z; };
x: 0*sizeof(int) = 0, y: 5*sizeof(char)=5, z: 6*sizeof(char)=6; tot = 2*4=8
c struct { char x; int y; char z; }
x: 0*sizeof(char) = 0, y: 1*sizeof(int)=4, z: 9*sizeof(char)=9; tot = 3*4=12