5. E-R Relationship
Design Procedure¶
设计一个数据库的时候,应该如下进行考虑

其中,每一步之间都是独立的。比如,使用 ER diagram 进行概念设计的时候,不需要考虑是关系型数据库,还是面向对象数据库,还是任何数据库。
- 我们只需要在具体的 logical design 中,进行 logical schema 的 design
Example: Conceptual Design¶

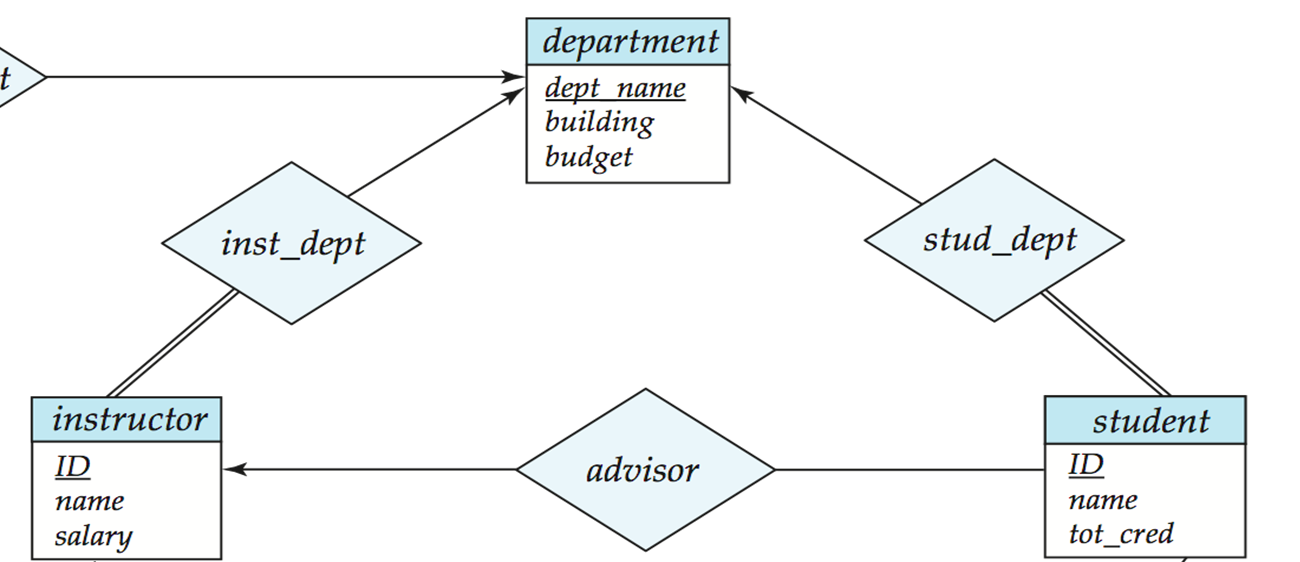
图例:
- 矩形就是一个实体(entity) 的集合。
- 解释: 实体就是类型相同,又可以相互区分(via primary key) 的 object
- 矩形里面的就是实体的属性
- 菱形就是两个实体之间的关系(relation)
- 带双线的菱形:见下
- 箭头
- 单箭头代表多对一
- 以 stud_dept 为例:每一个 dept 可以有多个学生
- 无箭头代表多对多
- 以 teaches 为例:一个 instructor 可以 teaches 多门课程,一门课程可以有多个 instructors
- 双箭头代表一对一(本图没有)
- 单箭头代表多对一
- 箭头的线
- 单线代表该实体集合的实体不一定都要建立关系
- 以 stud_dept 为例:一个 department 可能没有任何学生
- 以 teaches 为例:一个 instructor 可能不教任何课程
- 双线代表该实体集合的所有实体都必须建立关系
- 以 stud_dept 为例:任一学生必须属于一个部门
- 以 teaches 为例:任一课程必然被某个老师教
- 单线代表该实体集合的实体不一定都要建立关系
- 下划线
- 实线代表 primary key
- primary key 可能是一个 n-tuple,参考 time_slot
- 虚线意义:见下
- 实线代表 primary key
特殊图例:
- 如果一个 entity 的下划线是虚线,那就代表:这个 entity 是一个弱实体 (weak entity)
- 意思就是:这个 entity 的属性不足以让实体之间可以相互区分,因此需要依赖另一个(强)实体(依赖关系用带双线的菱形表示)。即,除了划了下划线的这些属性(称为 discriminator),还需要另一个强实体的 primary key,才能组成这个弱实体的 primary key
- 如 OOP、DBMS 都可以有同样年份学期的 1 班
- 因此需要依赖具体的 course_id 来区分不同的 entity
- 但是,由于 course_id 放在 section 下面,就会出现冗余,因此我们选择让 section 依赖于 course 存在
- 意思就是:这个 entity 的属性不足以让实体之间可以相互区分,因此需要依赖另一个(强)实体(依赖关系用带双线的菱形表示)。即,除了划了下划线的这些属性(称为 discriminator),还需要另一个强实体的 primary key,才能组成这个弱实体的 primary key
- 一个关系可以带有属性
- 比如 takes 关系的 grade 属性(i.e. 学生上这门课的课程成绩)
Relationship Sets¶
Relationship sets 就是一个 n-ary relationship:\(\set{(e_1, \dots, e_n)|e_1\in E_1, \dots, e_n\in E_n}\)
通常而言,对于两个 entity 而言,如果关系中不含属性,那么就是一个二元关系(\(E_1, E_2\) 分别对应两个 entity 的 primary key)。
如果关系中含有属性,那么就是 (2+# of attributes) 元关系。
多元关系二元化¶

方法:把多元联系实体化。如 proj_guide 里有老师、学生、工程的 id. 随后这个实体又和另外三个实体各有一个二元联系。
Attributes¶
Attribute types:
- Simple(简单) and composite(复合) attributes.
- Single-valued(单值) and multivalued(多值) attributes
e.g. multivalued attribute:
phone_numbers, which is a list - Derived(派生)attributes
- Can be computed from other attributes
e.g.
age, givendate_of_birth
- Can be computed from other attributes
e.g.
Redundant Attributes¶
如果一个 attributes 在两个实体中均有出现,那么,就把其中不是 primary key 的实体的 attributes 删去。具体如下:

Example¶


Reduction to Relational Schemas¶
Representing Entity Sets¶
对于 strong entity set,就原原本本即可
- 用 ER 图里的 attributes 当作 relational schemas 的 attributes
- 用 ER 图里的 primary key 当作 relational schemas 的 primary key
对于 weak entity set,
- 用 ER 图里的 attributes 当作 relational schemas 的 attributes
- 用 ER 图里自己的 discriminator + 依赖实体的 primary key 当作 relational schemas 的 primary key
Representing Relationship Sets¶
对于 many-to-many,relationship 就使用一个含有两个属性的 relational schema 来管理。
- 因为 relationship 就是集合,因此必须用一个集合来管理
- 另外,relationship schema 需要有 foreign key 指向两个集合的对应 primary key
对于 many-to-one,除了额外定义一个 relational schema 以外,还可以把 relational schema 与 "many" 的一方进行合并,从而避免使用一个额外的 relational schema
-
因为 relationship 可以视作一个函数,而 "many" 的一方就是定义域,因此我们可以直接在 "many" 添加对应的值
如上图,我们可以直接在 instructor 和 student 处增加 dept_name,从而避免定义 inst_dept 和 stud_dept 这两个表
Composite, Multivariate and Derived Attributes¶
Composite attributes 就是 C 中的 struct。由于关系型数据库只支持 simple attributes,因此 composite attributes 必须被 "flatten"。
Multivariate attributes 的典型例子,就是 list。由于 list 并不能被简单展开,因此我们新建一个 E(ntity)M(ultivariate) Schema 来处理。
但是在面向对象数据库中,就可以当作一个 object 存下来,会自然很多。
另外,derived attributes 在关系型数据库中,也只好当作一个简单数据类型来处理。
- 比如,
data_of_birth就是time().year - birth_year,每过一年,我们必须更新一次
但是在面向对象数据库中,就可以当作一个函数存下来,会自然很多。
Design Issues¶
Common Mistakes in E-R Diagrams¶
-
信息冗余 student 的
dept_name应该去掉
-
关系属性使用不当 这里一门课可能有很多次作业,不能只用一个实体。

解决方法:

Use of entity sets vs. attributes¶

- 第一种方法,明确放一个电话号码。
- 第二种方法,电话号码可以附属更多属性,一个电话号码可以由多人共享。(如办公室的公共电话)
Use of entity sets vs. relationship sets¶
Possible guideline is to designate a relationship set to describe an action that occurs between entities.

实体可以便于与其他实体建立联系。
如电商,我们可以简单的把客户和商品用 buy 联系起来,但后续还会有付款、物流等情况,我们最好把 buy 实体化为订单。
Placement of relationship attributes¶

- 第一种方法,可以记录每次访问的访问日期。
- 第二种方法,只能记录用户最近一次访问日期,不完整。
Binary Vs. Non-Binary Relationships¶
-
Binary versus n-ary relationship sets Although it is possible to replace any nonbinary (n-ary, for 𝑛>2) relationship set by a number of distinct binary relationship sets, a n-ary relationship set shows more clearly that several entities participate in a single relationship.
-
Some relationships that appear to be non-binary may be better represented using binary relationships e.g. A ternary relationship parents, relating a child to his/her father and mother, is best replaced by two binary relationships, father and mother Using two binary relationships allows partial information (e.g. , only mother being know) But there are some relationships that are naturally non-binary e.g. :
proj_guide